what's tyre pyrolysis plant
2025-02-24 15:45:00
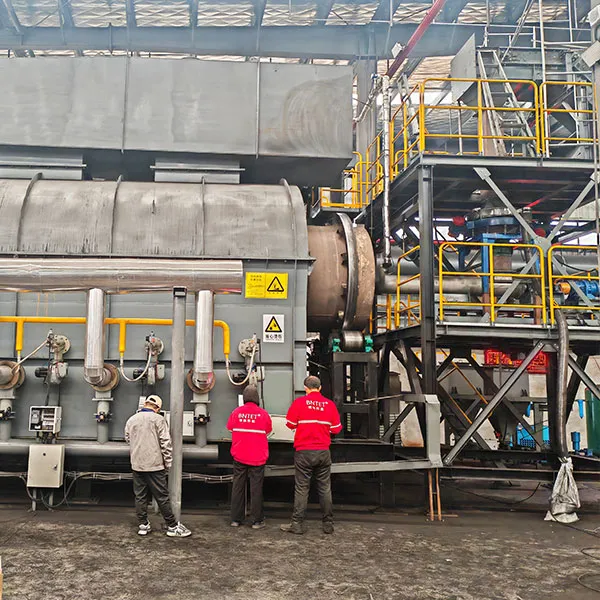
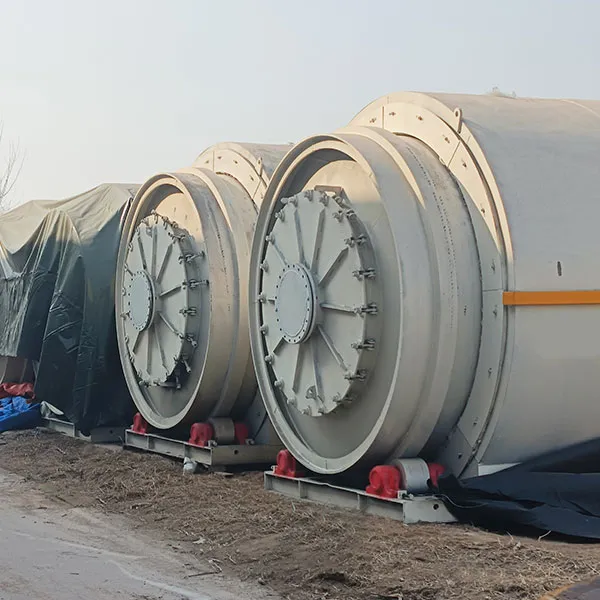
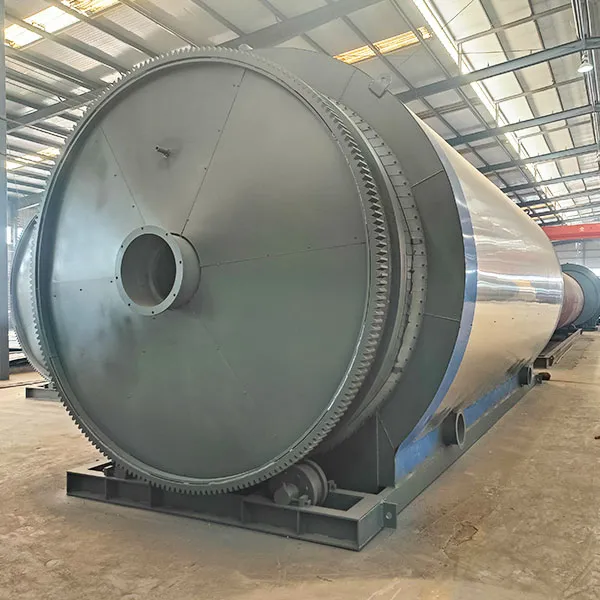
A tyre pyrolysis plant is a specialized facility designed to convert waste tires into useful products through the process of pyrolysis. Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen. In the context of a tyre pyrolysis plant, the organic material is waste tires.
Here's a general overview of how a tyre pyrolysis plant works and the products it can generate:
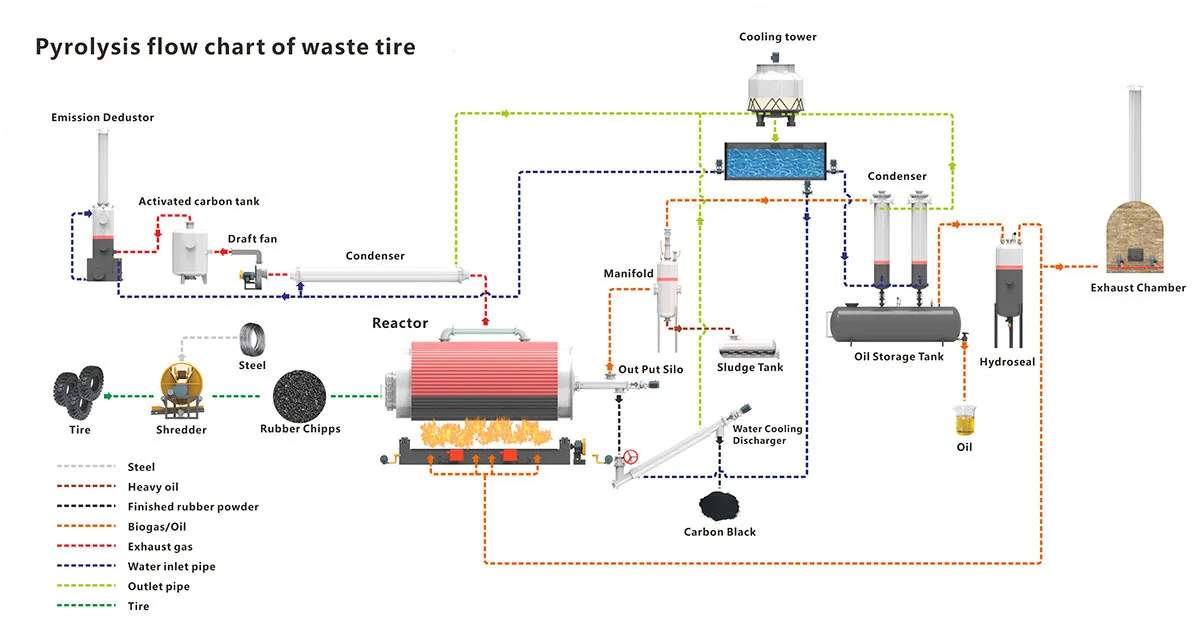
Feeding: Waste tires are fed into the pyrolysis reactor. The size of the tires may be reduced to facilitate the process.
Pyrolysis: The reactor is heated to a high temperature (typically between 250°C and 500°C) in the absence of oxygen, causing the rubber in the tires to break down. This process produces a mixture of gases, liquids, and solids.
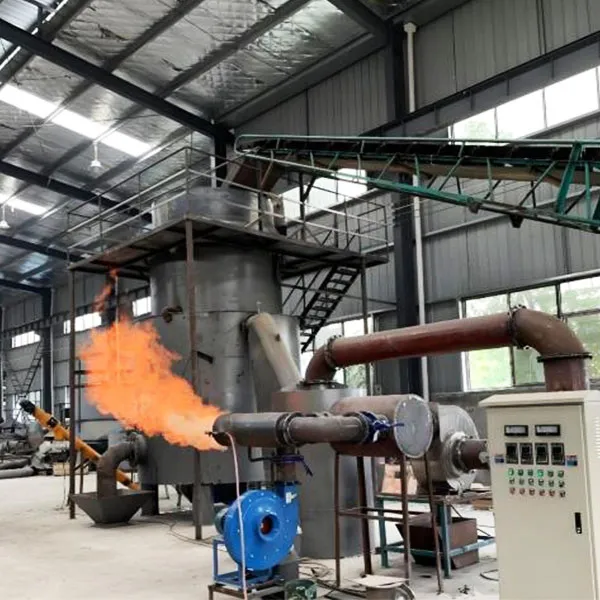
Cooling and Condensation: The gases produced during pyrolysis are cooled and condensed into a liquid form, which is often referred to as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
Gas Recovery: Non-condensable gases are collected and can be used to fuel the pyrolysis process, making the plant more energy-efficient.
Solid Collection: The solid residue from the pyrolysis process is carbon black, which can be used as a reinforcing agent in new rubber products, as a pigment, or as a fuel.
Steel Recovery: Tires contain steel wires, which are separated and can be recycled.
The main products of a tyre pyrolysis plant are:
Pyrolysis Oil: Can be used as a fuel or further refined into diesel.
Carbon Black: Used in various industrial applications.
Steel Wire: Recycled for use in new products.
Syngas: Can be used to generate electricity or heat.

Tyre pyrolysis plants are considered an environmentally friendly solution to the problem of waste tire disposal, as they help reduce the number of tires in landfills and can recover valuable materials and energy from waste. However, the operation of such plants must be carefully managed to ensure that emissions are controlled and that the process is safe and environmentally sound.






